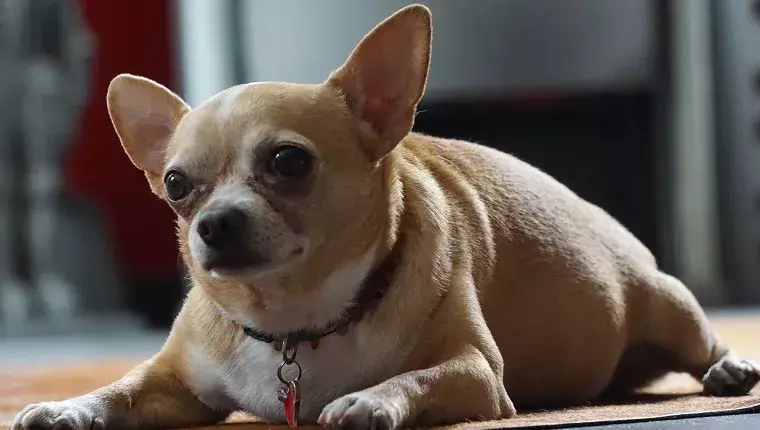
Obesity is not only a problem for humans but has become a pressing issue in the canine population as well. Recent findings reveal that a staggering 56% of dogs in America are classified as overweight or obese, leading to concerning implications for their longevity. A study examining data from 50,000 dogs across a dozen breeds highlights that these overweight canines may face life expectancy reductions of up to 2.5 years. When translated into human terms, this alarming statistic signifies a loss of approximately 10 to 15 years of potential life. It’s evident that the health of our furry companions is at stake, yet many owners are oblivious to the gravity of this situation.
Similar to humans, dog obesity is assessed using the Body Mass Index (BMI) standard, which evaluates appropriate weight in connection with height. In the case of our canine friends, a dog that weighs 15% above its ideal weight is classified as overweight, while those 30% or more above the standard are categorized as obese. Unfortunately, there isn’t a universal standard for ideal canine weight due to variances across different breeds. Therefore, while one dog might be perfectly healthy at a certain weight, another of the same breed may be considered unhealthy. Consulting with a veterinarian is crucial to navigating this complex landscape of ideal body weight.
The consequences of obesity extend far beyond mere aesthetics; they substantially impact the quality of life and general health of dogs. Conditions like arthritis become prevalent due to the excessive strain on their joints. Moreover, obese dogs may find themselves more susceptible to injurious conditions, such as torn ligaments—issues that could mandate surgical interventions. Respiratory and cardiovascular problems are also rampant among overweight dogs, leading to further complications. Collectively, these health challenges threaten the overall well-being and lifespan of our beloved pets.
As guardians of these animals, dog owners must take proactive steps to prevent obesity. Establishing regular and controlled feeding schedules is vital, as is ensuring that dogs participate in regular physical activity. Tailoring exercise routines to be enjoyable yet effective will foster a healthier lifestyle. Importantly, pet owners should liaise closely with their veterinarians to devise individualized wellness plans that encompass nutrition and physical exercise.
Combating canine obesity requires vigilance, commitment, and an understanding of the unique needs of each dog. It is our responsibility to create an environment that promotes healthy living. Ultimately, reducing obesity not only enhances the quality of life for dogs but can also extend their years of companionship with us. As dog owners, we must reflect on the practices we implement daily—are they conducive to keeping our dogs healthy? Monitoring weight and encouraging an active life are crucial steps in safeguarding our furry friends’ health and happiness.