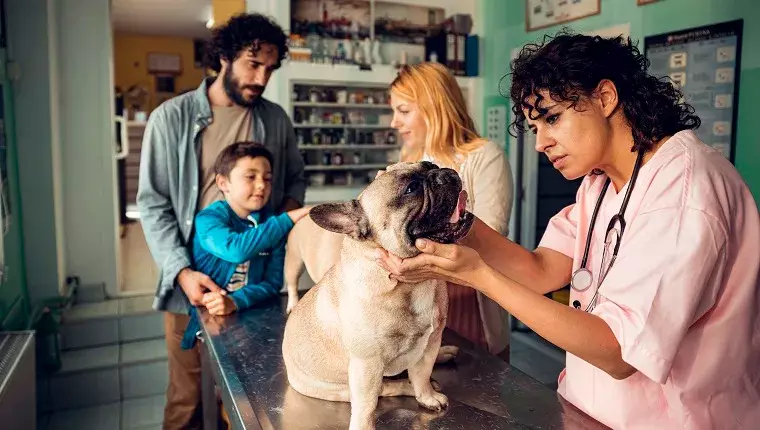
Abnormal molar development in dogs is a significant dental health issue manifesting mainly in smaller breeds. Specifically referred to as dilacerated mandibular first molar, this condition arises when a dog’s molar teeth encounter spatial constraints, inhibiting proper growth. Dogs with this problem may exhibit a range of symptoms that hint at underlying dental distress. Early recognition is crucial, as untreated dental issues can escalate, leading to severe discomfort and complicated health scenarios.
When it comes to recognizing the signs of abnormal molar development, pet owners should be vigilant about several oral health indicators. Common symptoms may include receding gums, gum inflammation, bleeding, reduced appetite, and difficulty in chewing or eating. Observing your dog closely for these signs is essential because they can indicate not just dental pain but general discomfort that may affect their quality of life. Should you notice any of these symptoms, seeking professional veterinary care promptly can lead to a timely diagnosis and intervention.
The primary cause of abnormal molar development is the absence of adequate space in the jaw for the molars to grow normally. Factors such as genetics may predispose certain breeds to this condition, making them more susceptible to dental malformations. Additionally, trauma to the mouth caused by accidents or rough play can lead to displacement or abnormal alignment of the teeth. Breeds particularly at risk include well-known small dogs like Boston Terriers, Pugs, and French Bulldogs, emphasizing the importance of dental vigilance for owners of these breeds.
If a dog owner suspects their pet may be suffering from this dental disorder, the initial step is visiting a veterinarian. During the consultation, the vet will conduct a thorough physical and oral examination, assessing the dog’s mouth for any noticeable signs of distress. They may inquire about the dog’s dietary habits and any recent injuries that might have impacted the area. To confirm the diagnosis, diagnostic tools such as dental X-rays are often employed, giving the veterinarian a clearer view of the dental structure and any abnormalities present.
Treatment strategies for abnormal molar development vary based on the severity of the symptoms. For immediate relief, pain management may involve prescribed medications to alleviate discomfort. In more severe cases, the extraction of the affected tooth may be recommended to prevent further complications. Post-treatment care is equally important; modifications to the dog’s diet may be necessary to ensure they can eat comfortably and without pain during their recovery. It is crucial for pet owners to adhere strictly to their vet’s medication guidelines to ensure a successful recuperation.
Being proactive about dental health is vital for dogs, especially those predisposed to dental abnormalities like molar development issues. Regular check-ups, dental cleanings, and conscious attention to symptoms are key elements in keeping your furry friend’s mouth healthy. By understanding the signs and treatment options for abnormal molar development, dog owners can take a more active role in ensuring their pets lead comfortable, healthy lives. Always consult your veterinarian when in doubt—your dog’s dental health is worth the investment of time and care.