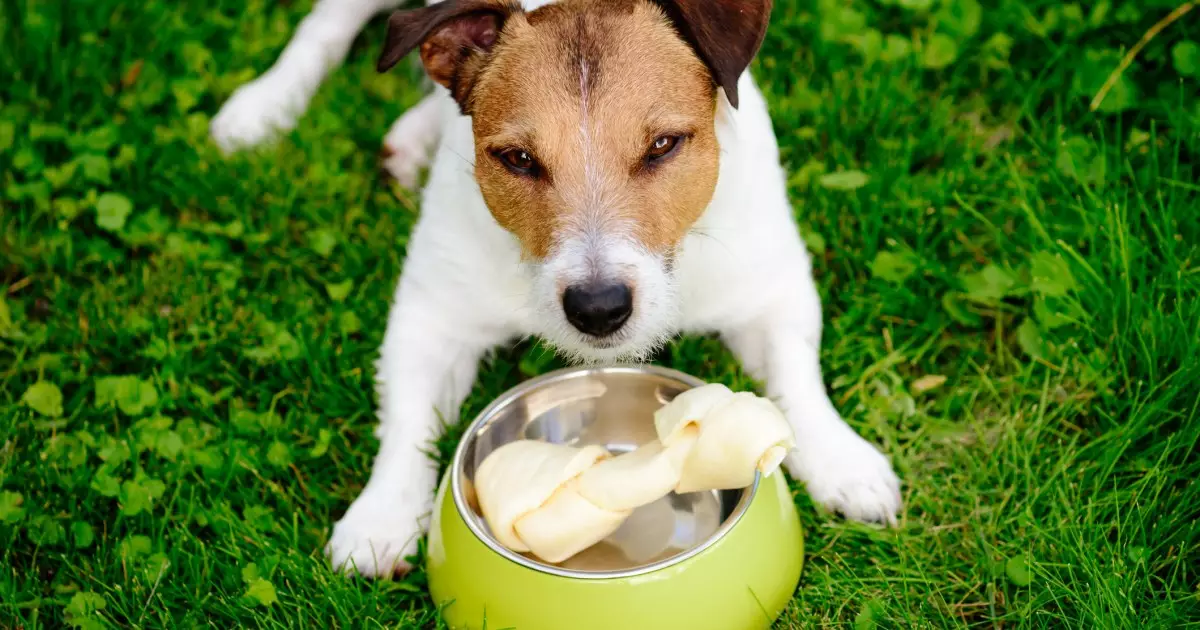
Resource guarding is a perplexing behavior exhibited by many dogs, embodying their instinctual drive to protect what they consider valuable. This article will delve deep into the phenomenon of resource guarding, outlining its causes, manifestations, and the most effective ways to address it, ensuring both the safety of the canine and the comfort of their human companions.
Resource guarding occurs when a dog displays protective behaviors towards items they hold dear, which commonly include food, toys, or specific resting spots within the home. This behavior can be understood through a straightforward lens: dogs, being instinctual creatures, strive to preserve their possessions from perceived threats. For example, consider a Cocker Spaniel that growls when approached during mealtime or a Labrador Retriever that snaps when someone reaches for its favorite toy. The growling, lip curling, and freezing behavior are indicative of a dog that feels threatened and reinforces their intent to protect what they value.
At the heart of resource guarding is the dog’s instinct to stave off loss. In the wild, this protective behavior is crucial for survival, as losing one’s food or safe space could have dire consequences. However, these behaviors can also be learned responses influenced by past experiences. A dog’s interpretation might be as logical as, “Last time someone approached my toy, it was taken away. I must guard it fiercely now.” Understanding this viewpoint is crucial for owners aiming to modify such behaviors effectively.
Before diving into corrective techniques, it’s essential to acknowledge the potential danger that resource guarding presents. Intervening improperly can lead to bites or aggressive interactions, especially if an owner attempts to take away an item that the dog feels compelled to protect. Consequently, working on resource guarding issues requires the oversight of a trained dog behaviorist or an experienced trainer who can provide a structured approach to desensitization while ensuring everyone’s safety.
Desensitization is widely regarded as the most humane and effective strategy for mitigating resource guarding behaviors. The concept revolves around creating positive associations between the dog and the presence of humans near their valued items. Instead of employing punitive measures—like scolding or physically attempting to remove the item—owners should focus on gradually forming a positive connection through novel techniques.
A fundamental exercise involves the dog’s mealtime. Initially, maintain a safe distance that allows you to observe the dog eating without triggering any guarding responses. Introduce an enticing treat that surpasses their meal’s value, ensuring that the dog’s focus shifts from guarding to anticipating a positive experience. Over time, as the dog becomes more comfortable, you can gradually decrease the distance and incorporate various angles, fostering an environment where proximity is associated with rewards rather than threats.
Another exercise involves using toys, albeit not the dog’s favorites at first. Start by picking up a less valued toy while simultaneously presenting a high-value treat. This encourages the dog to release the toy in exchange for something even better, reiterating the notion that giving up possessions can lead to positive outcomes.
Similarly, addressing resource guarding related to a dog’s resting spot—like their bed—requires patience and positive reinforcement. Approach with a highly desirable treat that the dog can sense from a distance, rewarding them while they remain in their space. This method helps to reinforce the idea that humans approaching their beloved area brings good things, further diminishing protective instincts.
It’s important to note that these exercises will require time—often weeks—to see profound changes. Consistency is key; incorporating these exercises early, especially during a puppy’s developmental phases, can promote a healthier mindset towards resource sharing. Commands like “off” and “leave it” can be implemented alongside treats of greater value than what is under guard, empowering the dog to learn that surrendering resources results in gain rather than loss.
Ultimately, a holistic approach to managing resource guarding involves spaying or neutering pets, which has been shown to lead to more balanced dispositions and reduces aggressive tendencies associated with guarding. The complexity of resource guarding behavior is not merely rooted in instinct; it is intertwined with the dog’s experiences and the environment they inhabit.
Through dedicated and compassionate training, owners can help their pets develop a sense of security around their treasured items. As dogs grow comfortable with the human presence alongside their resources, they become more relaxed, fostering a harmonious home environment. Resource guarding is a manageable issue, provided it is approached with understanding, strategy, and an unwavering commitment to the dog’s well-being.