Maintaining a pet’s oral hygiene is often overlooked by many dog owners, despite its crucial importance. Gingivitis, an inflammation of the gums, is a prevalent issue that can lead to more serious dental diseases if neglected. This article aims to provide a thorough understanding of gingivitis in dogs, its symptoms, causes, treatments, and preventive measures, enabling pet owners to ensure their dogs maintain optimal oral health.
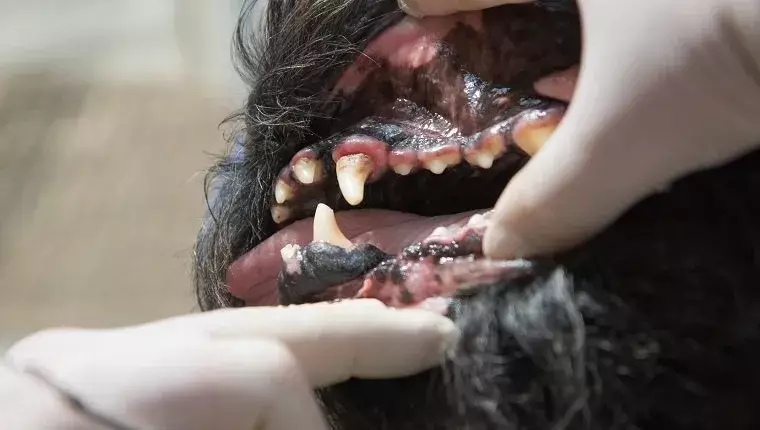
Gingivitis is the initial stage of periodontal disease, characterized by the inflammation of the gums surrounding the teeth. It is a common condition in dogs and occurs when plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—accumulates on the teeth. If this buildup is not taken care of, it can harden into tartar, leading to further complications such as periodontal disease, which can ultimately result in tooth loss. Understanding gingivitis is essential for dog owners to recognize signs early and seek appropriate treatment.
The symptoms of gingivitis can range from mild to severe and may manifest in various ways. Initially, you might notice a thin red line along the edge of your dog’s gums, which is an early indicator of inflammation. As the condition progresses, other symptoms may become apparent, including:
– Swollen and tender gums
– Persistent bad breath
– Visible plaque and tartar buildup on teeth
– Gums that bleed, particularly during brushing
– Pus or discharge from the gum area
– Signs of discomfort or pain when eating
– Increased drooling or reluctance to eat
– Loose or receding teeth
If you observe any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult a veterinarian for an accurate diagnosis and prompt treatment.
The leading cause of gingivitis in dogs is poor dental hygiene, underscoring the need for regular oral care. When food particles are not cleaned away, they combine with bacteria in the mouth, forming plaque. Over time, plaque hardens into tartar, further irritating the gums. Certain breeds, especially those with crowded teeth like toy breeds, are predisposed to gingivitis. Additionally, dogs that groom themselves often can face elevated risks due to the buildup of bacteria from saliva.
Other contributing factors can include a poor diet lacking essential nutrients, which can compromise a dog’s immune system, increasing susceptibility to dental diseases. Therefore, maintaining a balanced diet is vital for overall health, including oral hygiene.
If your dog is diagnosed with gingivitis, the first step usually involves a professional dental cleaning. During this procedure, a veterinarian removes tartar and plaque and polishes the teeth to reduce future adherence of bacteria. Depending on the severity of the condition, your dog may need to undergo this cleaning under anesthesia.
In cases where gingivitis has led to a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be required to eliminate the infection and promote gum healing. After professional treatment, your vet will likely recommend at-home care, which could include special toothpaste and dental rinses designed explicitly for dogs. Regular brushing at home, ideally several times a week, can significantly reduce plaque buildup and prevent further gum disease.
Preventing gingivitis is much more manageable than treating it. Regular at-home dental care is essential. Here are some effective ways to maintain your dog’s dental health:
– **Daily Brushing:** Aim to brush your dog’s teeth at least several times a week using a toothpaste formulated for dogs. Consistency is key to preventing plaque buildup.
– **Dental Chews and Toys:** These can aid in scraping off plaque and providing mechanical cleaning while your dog chews.
– **Routine Veterinary Check-ups:** Schedule regular veterinary visits that include dental check-ups and cleanings to catch potential issues early.
– **Diet:** Incorporating a high-quality diet that supports dental health can also be beneficial. Some commercial dog foods and treats are designed specifically to combat plaque.
By committing to routine dental care and staying vigilant about your dog’s oral health, you can significantly mitigate the risks associated with gingivitis and periodontal disease. Remember, maintaining your dog’s dental hygiene is just as crucial as other aspects of their health.