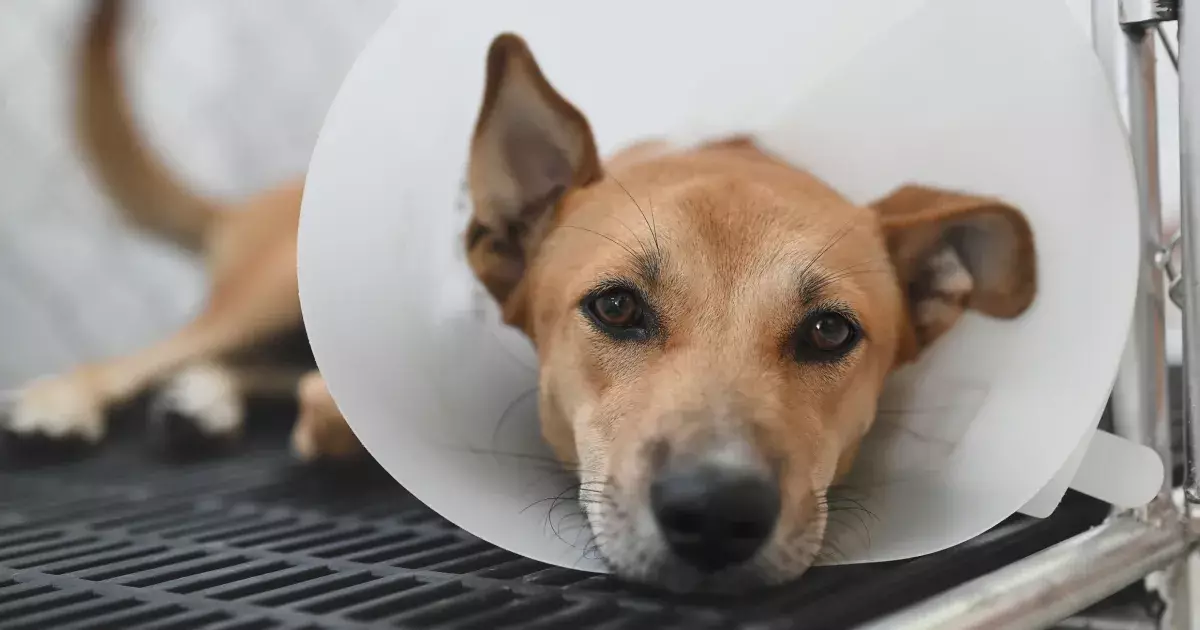
After your beloved pets undergo spay or neuter surgery, it’s crucial to understand the behavioral shifts that may occur as a result of anesthesia and the surgical procedure itself. In the immediate aftermath of surgery, you can expect your puppies to be somewhat subdued, each experiencing lingering effects from the anesthesia. This lethargy may last anywhere from 24 to 48 hours, during which time their typical spirited personalities might appear dulled. It’s common for dogs to display decreased engagement with their environment and may even prefer to sleep more than usual as their body recovers.
During this critical post-operative period, changes in appetite are also prevalent. Your pups might not exhibit the same enthusiasm for food as they usually do, which can be concerning for pet owners. Additionally, it’s worth noting that the incision site may be sensitive, causing discomfort. As such, to alleviate the urge to lick at the stitches and to help prevent any risk of infection, it is advisable to utilize a protective cone around their neck until the sutures are removed—typically within two weeks.
Long-Term Adjustments and Behavioral Outcomes
Transitioning to the long-term outcomes of spaying and neutering, it is essential to recognize that while some dogs exhibit positive changes post-surgery, others might experience more complex modifications in behavior. One of the most noted long-term changes is a tendency for weight gain. This can be attributed to altered metabolism and hormonal fluctuations following surgery. Consequently, pet owners should be prepared to adjust feeding regimens, possibly switching to a light diet once their pets reach adulthood to maintain a healthy weight.
Behaviorally, spaying and neutering often contribute to a calmer demeanor in dogs. For instance, male dogs that undergo neutering, especially at a younger age, may demonstrate reduced aggression and territorial tendencies. Conversely, dogs that are neutered later in life might retain some of their previous habits, making it more challenging to alter their behavior.
Despite these potential transformations, it’s important to remember that behavioral development will vary based on factors such as age, breed, and individual personality. While some dogs may gradually become more relaxed in the months following surgery, others may necessitate additional training or socialization efforts to assist in adjusting their behavior positively.
Navigating the Post-Surgery Journey
As a responsible pet owner, understanding the implications of spaying and neutering goes far beyond the surgery itself. Building a supportive environment for your recovering pups is essential. Monitoring their healing and behavioral changes in the weeks following surgery provides insight into their adjustment process. By being attuned to their needs—both physically and emotionally—you can facilitate a smooth transition to your dog’s new life stage and ensure they flourish as healthy, well-adjusted companions. While you may notice behavioral shifts in your dogs post-surgery, these changes can be managed effectively with care, attention, and a bit of patience.