Maintaining a healthy weight in dogs is a crucial responsibility for pet parents, especially following spaying or neutering. While these procedures are essential for enhancing the health, safety, and longevity of our canine companions, they can inadvertently lead to unwanted weight gain if not managed carefully. In this article, we will explore the implications of weight gain post-surgery, the biological factors at play, and effective strategies to keep your dog fit and healthy.
Spaying and neutering are common practices among dog owners, celebrated mainly for their wide array of health benefits. These procedures help mitigate the risks of certain diseases, reduce aggressive behaviors, and can lead to a longer, healthier life for dogs. Nonetheless, many new pet parents may not fully understand that spaying and neutering can trigger physiological changes that influence a dog’s metabolism and appetite regulation.
Research suggests that dogs, particularly males, may experience increased difficulty regulating their hunger after being neutered. This change can create a predisposition for obesity, which is concerning, given that an overweight dog is likely to face a myriad of health complications. Additionally, maintaining a proper exercise regimen alongside a balanced diet becomes an essential part of post-operative care.
Scientific studies indicate a pronounced risk of obesity in dogs that have undergone these surgeries, with larger breeds particularly vulnerable. The process of castration has been specifically linked to a significant increase in appetite, often coupled with a decreased motivation for physical activities. Veterinary experts, including those from the University of Copenhagen, warn that these changes can result in dogs consuming more calories than they expend, leading to weight gain.
Moreover, overweight dogs tend to have shorter lifespans — some research shows a decrease of up to two years compared to their healthier counterparts. This stark statistic highlights the importance of vigilance and proactive management in light of these potential outcomes.
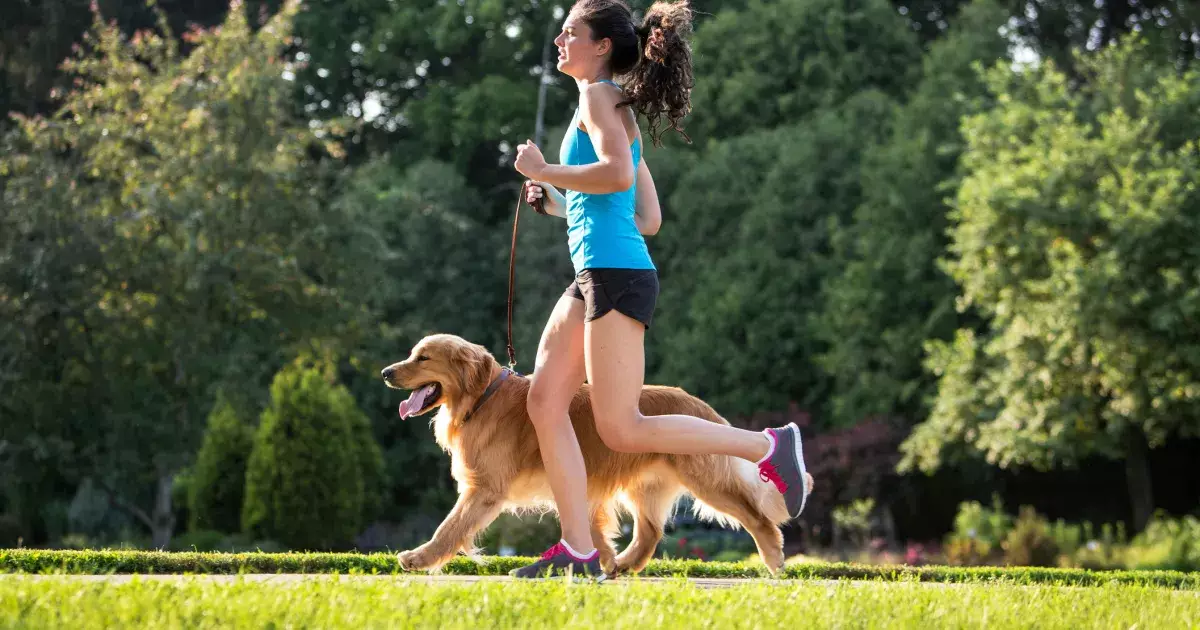
Keeping your dog at a healthy weight requires a concerted effort on the part of pet parents. One key strategy is instituting a regular exercise routine. Daily walks, active play, and even joining you on jogging excursions can ensure your dog remains physically engaged. Diverse activities not only stimulate your dog mentally but also help maintain their physical condition.
Another essential component is diet management. It is crucial to avoid common pitfalls such as free feeding or overindulgence in treats, especially those derived from the human diet. Establishing portion control is vital; consult your veterinarian to determine the ideal nutritional needs specific to your dog’s breed, age, and size. Implementing a structured feeding schedule can aid in weight management as well.
It’s also important to recognize the visual indicators of a healthy body condition in dogs. A dog should not have an excessively round shape; rather, they should exhibit a defined waist when viewed from the side or above. Their ribs should be palpable without excessive fat covering them. If visual assessments raise concern, seeking advice from your veterinarian can facilitate the right feeding and exercise adjustments.
Regardless of whether your dog is overweight, consistent engagement in active play should be prioritized. Activities such as fetch, tug-of-war, and canine agility exercises can foster a bond with your pet while ensuring they stay fit. Even simple activities, like hide-and-seek or interactive toys, can motivate your dog to remain active and mentally stimulated.
Furthermore, owners should remain mindful of their dog’s behavior and settings that may lead to overeating. Adjusting the environment—such as removing constant access to food bowls—can help establish better eating habits in dogs. Tracking your dog’s weight progress and body condition will also enable timely intervention if any weight gain trends arise.
Spaying and neutering can have significant implications for a dog’s weight and overall health. A holistic approach that incorporates diet, exercise, and awareness of your canine friend’s physical condition will go a long way in preventing obesity. Pet parents have a crucial role in ensuring their dogs remain healthy and happy companions for years to come. By staying informed and proactive, we can safeguard the well-being of our pets long after they’ve undergone surgery.